The pentobarbital formula is C11H18N2O3, representing its chemical makeup as a barbiturate derivative. This formula defines the arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms that give pentobarbital its sedative and hypnotic properties. It is a short-acting barbiturate, meaning that it works quickly but does not remain in the system for extended periods compared to longer-acting compounds. The pentobarbital formula provides the foundation for understanding its pharmacological action, as the molecular structure is closely tied to how the drug interacts with receptors in the brain. Its composition makes it effective as a central nervous system depressant, influencing neuronal activity to produce sedation, anesthesia, or seizure control in clinical settings.
Pentobarbital Drug Class and Mechanism of Action
Understanding the pentobarbital drug class helps explain its therapeutic uses and risks. Pentobarbital belongs to the class of barbiturates, which are central nervous system depressants. These drugs act primarily on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors, enhancing inhibitory signals in the brain. This results in sedation, reduced anxiety, hypnosis, or in some cases, anesthesia. The pentobarbital drug class was once widely used for insomnia and anxiety treatment but has since been largely replaced by benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine sedatives due to safety concerns. Nevertheless, pentobarbital continues to be used in specialized medical and veterinary contexts, particularly where strong sedation or anticonvulsant effects are required. Its classification highlights both its value in medicine and the strict controls imposed because of its potential for dependence and overdose.
Natri Pentobarbital and Its Applications
The term natri pentobarbital refers to sodium pentobarbital, the sodium salt form of this barbiturate that is more soluble in water and thus suitable for injectable solutions. Natri pentobarbital has been utilized in both human and veterinary medicine, often for anesthesia, sedation, and seizure management. In veterinary practice, it remains commonly used for humane euthanasia due to its effectiveness and reliability. The availability of natri pentobarbital in injectable form allows precise dosing, which is critical in professional settings. However, outside of controlled medical environments, its potency makes it extremely dangerous. Natri pentobarbital illustrates how modifications of the parent compound expand its clinical usability while still carrying the same need for strict regulation.
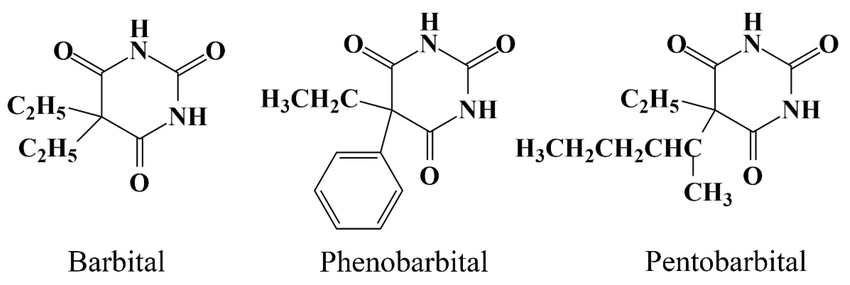
Pentobarbital Structure and Pharmacological Properties
Examining the pentobarbital structure provides insight into how this compound achieves its effects. Pentobarbital is a derivative of barbituric acid, and its structure includes side chains that determine its lipid solubility and duration of action. The higher lipid solubility of pentobarbital allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier quickly, explaining its rapid onset as a sedative. The pentobarbital structure also accounts for its short-acting nature compared to longer-acting barbiturates. By understanding the relationship between molecular structure and pharmacological action, researchers and clinicians can better predict its effectiveness, onset, and risks. This structural insight is a cornerstone in the development and refinement of sedative-hypnotic medications.
Pentobarbital Contraindications and Safety Considerations
Medical professionals must carefully weigh pentobarbital contraindications before prescribing or administering this drug. Contraindications include hypersensitivity to barbiturates, severe respiratory disease, liver impairment, and a history of substance abuse. Because pentobarbital depresses the central nervous system, it can worsen conditions such as sleep apnea or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It is also contraindicated in patients with a history of porphyria, a rare metabolic disorder that can be aggravated by barbiturates. Additionally, combining pentobarbital with alcohol, opioids, or other sedatives dramatically increases the risk of respiratory depression and overdose. Understanding pentobarbital contraindications ensures patient safety and emphasizes why its use is strictly supervised by medical professionals in both human and veterinary care.